 November 08, 2024
November 08, 2024
Ventilation systems play a critical role in maintaining indoor air quality (IAQ), removing contaminants, allergens, and other airborne particles. The effectiveness of a ventilation system often depends on the type of filters used, as different filters have varying levels of efficiency and purpose. Selecting the right filter for a ventilation system is essential, whether it’s for residential, commercial, industrial, or even specialized applications like cleanrooms and hospitals. In this article, we’ll explore the primary types of filters used in ventilation systems, their applications, and how they impact air quality and energy efficiency.
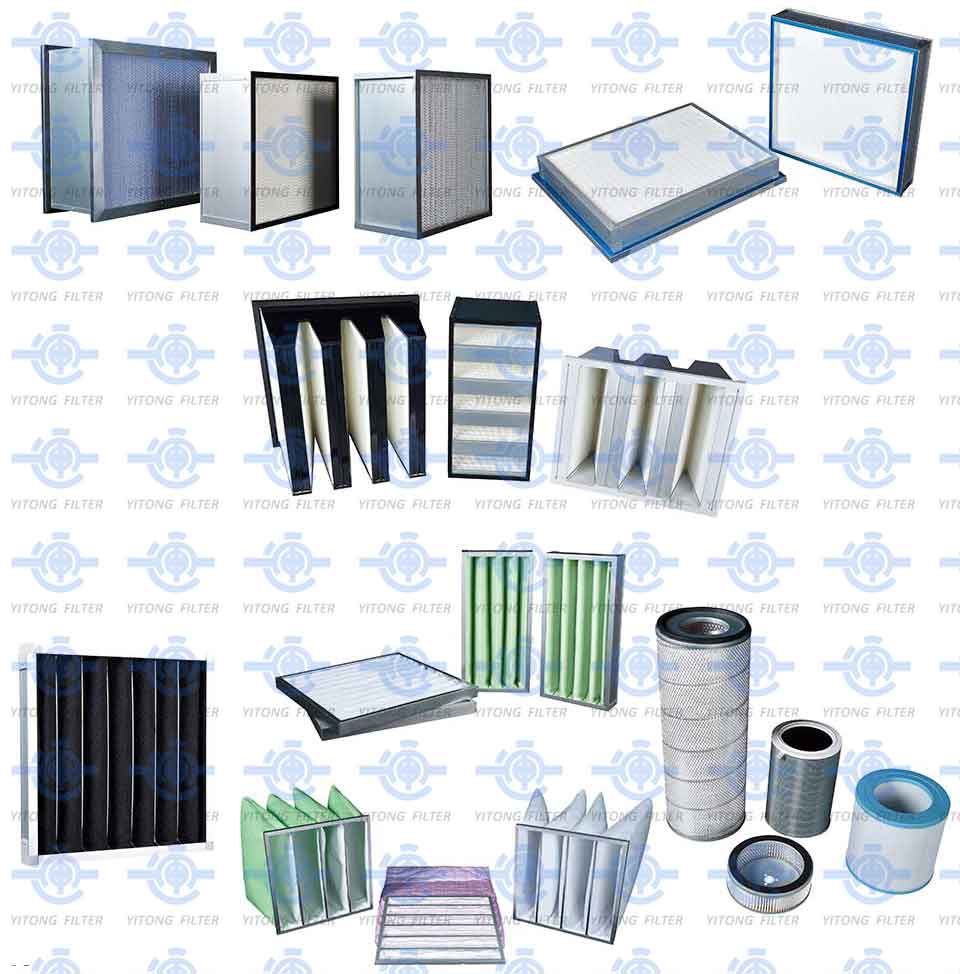

HEPA (High-Efficiency Particulate Air) filters are among the most popular and effective types of filters. Originally developed to capture radioactive particles in the 1940s, HEPA filters have since become essential in many ventilation systems due to their ability to remove up to 99.97% of airborne particles as small as 0.3 microns.
HEPA filters are commonly used in environments requiring high air purity, such as hospitals, laboratories, cleanrooms, and residential air purification systems. HEPA filters can be found in both industrial air filtration systems and commercial ventilation filters, providing essential protection in settings where contaminants can be harmful to health or products.
- High Efficiency: HEPA filters effectively capture dust, pollen, bacteria, and even some viruses.
- Long Lifespan: Although HEPA filters require regular maintenance, they generally have a longer lifespan than other filters.
- Ideal for Allergy and Asthma Control: Because they remove allergens from the air, HEPA filters are an excellent choice for people with respiratory conditions.
Carbon filters, also known as activated carbon filters, are designed to control odors and remove gases from the air. Unlike particulate filters, which trap solid particles, carbon filters use activated charcoal to absorb odors, chemicals, and volatile organic compounds (VOCs).
Carbon filters are widely used in residential air purification systems and commercial ventilation filters where odor control is essential, such as kitchens, restaurants, and industrial facilities with high VOC emissions.
- Odor Elimination: Carbon filters are highly effective at removing unpleasant smells, making them ideal for odor control in various settings.
- Chemical Filtration: These filters are useful for filtering out harmful gases, improving indoor air quality in spaces where chemicals are present.
MERV (Minimum Efficiency Reporting Value) is a rating system used to measure the effectiveness of air filters. MERV ratings range from 1 to 20, with higher ratings indicating a higher filtration level. MERV-rated filters are used in many HVAC (Heating, Ventilation, and Air Conditioning) air filters, with different MERV levels tailored for specific needs.
- Low-MERV Filters (1-4): Suitable for basic residential use, removing larger particles like dust and pollen.
- Mid-MERV Filters (5-8): Used in commercial ventilation filters, capturing smaller particles such as mold spores and pet dander.
- High-MERV Filters (9-16): Ideal for environments needing advanced air quality control, such as hospitals and cleanrooms.
- Customizable: MERV ratings allow you to select a filter that fits your specific filtration requirements.
- Wide Availability: MERV-rated filters are available for various applications, from residential to industrial air filtration systems.
Electrostatic filters use an electric charge to attract particles, making them a highly effective type of filter for capturing dust, smoke, and other pollutants. Some electrostatic filters are washable, which means they can be reused multiple times.
Electrostatic filters are commonly found in both residential and commercial ventilation systems. They are an eco-friendly option, especially in settings where replacing disposable filters frequently isn’t desirable.
- Reusable: Washable filters reduce waste and lower maintenance costs over time.
- Highly Effective: These filters effectively capture fine particles, contributing to cleaner indoor air.
Fiberglass filters are among the most basic and inexpensive options available. Made from layered fiberglass fibers, these filters can trap larger particles such as dust, lint, and hair but are less effective for smaller contaminants.
Fiberglass filters are often used in residential HVAC air filters for basic filtration needs. They are suitable for low-MERV applications and areas where only basic filtration is required.
- Affordable: Fiberglass filters are budget-friendly and widely available.
- Energy-Efficient: Because they offer less resistance to airflow, they are often more energy-efficient, although they require more frequent replacement.
Pleated filters consist of folded materials (usually polyester or cotton), which provide a larger surface area for trapping particles. They come in various MERV ratings and offer a balance of efficiency, durability, and airflow.
Pleated filters are commonly used in HVAC air filters for residential, commercial, and industrial applications. With a variety of MERV ratings available, pleated filters can be used in everything from standard home systems to hospital-grade air filters.
- Improved Filtration: The pleats increase the surface area, allowing the filter to capture more particles.
- Durable: Pleated filters last longer than non-pleated options, reducing maintenance frequency.
UV filters use ultraviolet light to kill bacteria, viruses, and other microorganisms. While they are not particulate filters, UV filters are often paired with HEPA or other filters in ventilation systems to enhance IAQ.
UV filters are commonly used in healthcare settings, laboratories, and cleanrooms where air sterilization is critical. They are also found in residential air purification systems as part of a multi-stage filtration process.
- Kills Microorganisms: UV light eliminates harmful pathogens, contributing to safer indoor air.
- Used in Conjunction with Other Filters: Often used with HEPA filters, UV filters provide an added layer of protection in air filtration systems.
Panel filters are simple, flat filters often used as pre-filters to capture larger particles before air reaches more advanced filtration stages. They come in various materials, including polyester, fiberglass, and synthetic fibers.
Panel filters are frequently used in HVAC air filters for residential and commercial applications, as well as industrial air filtration systems as the first line of filtration.
- Cost-Effective: Panel filters are generally inexpensive and easy to replace.
- Reduced Load on Advanced Filters: By capturing large particles, they extend the life of more expensive filters like HEPA or carbon filters.
When selecting a ventilation filter, it’s important to consider several factors, including the specific needs of the environment, the desired air quality level, and energy efficiency. Here are some tips for making the right choice:
- For Allergy Control: HEPA filters are ideal for residential air purification systems, capturing allergens like pollen, pet dander, and dust mites.
- For Odor Control: Carbon filters work well in environments with unpleasant smells, such as kitchens and industrial facilities.
- For High Air Purity: Hospital-grade air filters or high-MERV filters are best for healthcare and cleanroom settings, where maintaining excellent IAQ is essential.
- Eco-Friendly Options: Electrostatic and washable filters offer a sustainable alternative, reducing waste and the need for frequent replacements.
- Energy Efficiency: Lower-MERV fiberglass and panel filters allow for better airflow and reduce energy costs, making them suitable for systems where basic filtration is sufficient.
Regular maintenance is key to ensuring ventilation filters work effectively and prolong their lifespan. Here are some maintenance tips:
1. Regular Inspection: Check filters monthly, especially in high-traffic areas or environments with a lot of dust or pollutants.
2. Replace Filters as Needed: Each type of filter has its own recommended replacement schedule. For example, HEPA filters may last 6-12 months, while fiberglass filters may need replacement every 1-2 months.
3. Clean Reusable Filters: If you have washable or electrostatic filters, clean them according to the manufacturer’s instructions to maintain effectiveness.
From HEPA filters to electrostatic and UV options, there are various filters designed to meet specific needs in ventilation systems. By choosing the right filter, you can improve indoor air quality, control odors, and even reduce allergens, ultimately creating a healthier and more comfortable environment. Remember to consider factors like filter type, MERV rating, and specific IAQ needs when selecting a filter for your ventilation system, and ensure regular maintenance to keep it functioning at its best.

